Best Enterprise CRM Solutions
Best Enterprise CRM Solutions are crucial for businesses aiming to streamline operations and enhance customer relationships. This guide explores the leading platforms, essential features, and implementation strategies to help enterprises choose the optimal CRM system for their specific needs, ultimately driving growth and maximizing return on investment. We’ll delve into the nuances of enterprise-level requirements, comparing top contenders and addressing common challenges.
From defining your unique needs based on business size and operational goals to understanding the intricacies of implementation and integration, this comprehensive overview will equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision. We’ll also look at the future of enterprise CRM and how emerging technologies are shaping the landscape.
Defining Enterprise CRM Needs
Choosing the right CRM is crucial for any business, but the needs of an enterprise differ significantly from those of smaller organizations. Enterprise CRM solutions must handle a far greater volume of data, integrate with more complex systems, and support a much larger and more diverse user base. This necessitates a more robust and scalable system with advanced features tailored to the unique challenges of large-scale operations.
Enterprise CRM distinguishes itself from smaller-scale solutions through its capacity for handling vast amounts of data, intricate integrations, and sophisticated functionalities. It’s not simply a matter of scaling up a smaller CRM; enterprise-level solutions are architecturally different, prioritizing scalability, security, customization, and advanced analytics. This difference is reflected in the cost, complexity, and the level of IT support required.
Business Size and CRM Requirements
Different business sizes have varying CRM needs. Small businesses might only require basic contact management and sales tracking. Medium-sized businesses may need more advanced features like marketing automation and reporting capabilities. Large enterprises, however, demand comprehensive solutions that integrate with numerous internal systems and support complex workflows across multiple departments and geographical locations. For example, a small bakery might use a simple CRM to manage customer orders and loyalty programs, while a multinational corporation needs a system capable of handling millions of customer interactions, managing complex sales cycles across global teams, and providing real-time insights into market trends.
Critical Functionalities of Enterprise CRM Systems
Enterprise CRM systems require several key functionalities to effectively manage complex business operations. These include robust contact management, advanced sales force automation, comprehensive marketing automation, in-depth analytics and reporting, seamless integration with other enterprise systems (ERP, marketing automation platforms, etc.), robust security features to protect sensitive customer data, and scalability to accommodate future growth. Furthermore, effective customer service management, including features like ticketing systems and knowledge bases, is crucial. The ability to customize workflows and dashboards to meet specific business needs is also a vital aspect.
Comparison of CRM Needs Across Enterprise Sizes
| Feature | Small Enterprise | Medium Enterprise | Large Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Basic contact details, simple segmentation | Advanced contact details, multiple segmentation options, lead scoring | Comprehensive contact profiles, advanced segmentation, lead nurturing, 360-degree customer view |
| Sales Force Automation | Basic sales tracking, opportunity management | Advanced sales pipeline management, forecasting, sales analytics | Advanced sales pipeline management, forecasting, sales analytics, territory management, complex sales cycle support, CPQ (Configure, Price, Quote) integration |
| Marketing Automation | Basic email marketing | Automated email campaigns, lead nurturing workflows, social media integration | Advanced marketing automation, personalized campaigns, A/B testing, multi-channel marketing, campaign analytics |
| Reporting & Analytics | Basic sales reports | Customizable reports, dashboards, sales forecasting | Advanced analytics, predictive modeling, real-time dashboards, custom reporting, business intelligence integration |
| Integration | Limited integration needs | Integration with email, marketing automation tools | Seamless integration with ERP, marketing automation, other enterprise systems, APIs for custom integrations |
| Security | Basic security measures | Enhanced security measures, access control | Robust security features, data encryption, compliance with industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) |
| Scalability | Limited scalability requirements | Moderate scalability requirements | High scalability, ability to handle large volumes of data and users |
Top Enterprise CRM Platforms
Choosing the right enterprise CRM platform is crucial for business success. A well-implemented system streamlines operations, improves customer relationships, and ultimately drives revenue growth. This section will examine three leading platforms, comparing their features, pricing, scalability, and integration capabilities to help you make an informed decision.
Leading Enterprise CRM Platforms Overview
Several enterprise CRM platforms dominate the market, each offering a unique set of capabilities. Three prominent examples are Salesforce Sales Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SAP Customer Experience. These platforms cater to various business sizes and industries, providing comprehensive solutions for managing customer interactions and data.
Salesforce Sales Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SAP Customer Experience Comparison
The following comparison highlights key differences and similarities between Salesforce Sales Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics 365, and SAP Customer Experience. Each platform excels in different areas, making the choice dependent on specific business needs and priorities.
| Feature | Salesforce Sales Cloud | Microsoft Dynamics 365 | SAP Customer Experience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Features | Sales force automation, contact management, lead management, opportunity management, forecasting, reporting and analytics. Strong ecosystem of apps. | Sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service, field service, project service automation. Deep integration with Microsoft Office 365. | Comprehensive suite encompassing sales, service, marketing, commerce, and customer data platform. Strong focus on integration with other SAP solutions. |
| Pricing Model | Subscription-based, tiered pricing with various features and user licenses available. Can be expensive for large deployments. | Subscription-based, tiered pricing with various modules and licenses. Pricing can vary depending on chosen modules and users. | Subscription-based, typically enterprise-level pricing. Pricing is complex and often requires custom quotes. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, capable of handling massive data volumes and user bases. Offers cloud-based infrastructure for easy expansion. | Highly scalable, leveraging cloud infrastructure for flexibility and growth. Can accommodate large organizations and complex workflows. | Highly scalable, designed for large enterprises with complex requirements. Integrates well with existing SAP infrastructure. |
| Integration Capabilities | Extensive API and integration tools, allowing seamless connection with various third-party applications. AppExchange offers a vast library of pre-built integrations. | Strong integration with Microsoft products and services, as well as other third-party applications via APIs and connectors. | Strong integration capabilities within the SAP ecosystem. Offers APIs and integration tools for connecting with other systems. |
Pros and Cons of Each Platform
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each platform is essential for informed decision-making.
Salesforce Sales Cloud
- Pros: Extensive features, strong ecosystem, high scalability, robust reporting and analytics.
- Cons: Can be expensive, complex to implement, steep learning curve.
Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Pros: Seamless integration with Microsoft Office 365, user-friendly interface, relatively cost-effective compared to Salesforce.
- Cons: Customization can be limited, some features might require additional modules.
SAP Customer Experience
- Pros: Comprehensive suite, strong integration with other SAP solutions, ideal for large enterprises with complex needs.
- Cons: High cost, complex implementation, requires specialized expertise.
Key Features and Functionality
An effective enterprise CRM system goes beyond simple contact management. It integrates various crucial functionalities to streamline operations, enhance customer relationships, and drive business growth. The core features discussed below are essential for maximizing the return on investment from a CRM implementation. Their effective use contributes directly to improved sales, marketing efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Enterprise CRM platforms offer a comprehensive suite of tools designed to manage all aspects of customer interactions throughout the entire customer lifecycle. These features are not isolated modules; they work synergistically to provide a holistic view of the customer, enabling businesses to personalize interactions and optimize processes across different departments.
Sales Force Automation
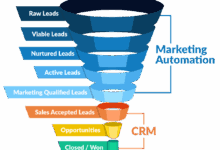
Sales force automation (SFA) streamlines sales processes, increasing efficiency and productivity. Key components include contact management, lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting. Effective SFA allows sales teams to focus on closing deals rather than administrative tasks. For instance, automated lead routing based on predefined criteria ensures that qualified leads reach the appropriate sales representative promptly, significantly improving response times and conversion rates. This automated lead distribution can be based on factors such as industry, company size, or geographic location. Real-time access to customer information empowers sales representatives to provide personalized and informed responses, leading to higher customer satisfaction and increased sales.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation tools within an enterprise CRM system enable businesses to automate repetitive marketing tasks, personalize customer journeys, and measure campaign effectiveness. Features such as email marketing, social media management, and campaign tracking provide valuable insights into customer behavior. A well-executed marketing automation strategy can lead to higher engagement rates, improved lead nurturing, and increased conversion rates. For example, automated email sequences triggered by specific customer actions, such as website visits or form submissions, can nurture leads through the sales funnel effectively. This targeted approach improves lead qualification and ultimately increases sales conversion.
Customer Service
Effective customer service is crucial for building and maintaining strong customer relationships. An enterprise CRM system enhances customer service by centralizing customer information, providing agents with a 360-degree view of each customer’s history and interactions. Features like ticketing systems, knowledge bases, and live chat support improve response times and resolve customer issues efficiently. This improved efficiency translates directly to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, a company using a CRM system with integrated live chat can offer immediate support to customers, addressing their questions and concerns in real-time, reducing frustration and improving their overall experience.
Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities provide valuable insights into business performance and customer behavior. Dashboards and custom reports allow businesses to track key metrics such as sales revenue, marketing ROI, and customer satisfaction. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making, optimized resource allocation, and improved business strategies. For example, sales managers can use CRM reports to identify top-performing sales representatives, pinpoint areas for improvement in the sales process, and forecast future sales accurately. This detailed analysis empowers businesses to adapt their strategies and maximize their potential for success.
| Key Feature | Functionality | Benefits | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Force Automation | Contact management, lead management, opportunity tracking, sales forecasting | Increased sales efficiency, improved lead conversion rates, better sales forecasting | Automated lead assignment based on territory and industry |
| Marketing Automation | Email marketing, social media management, campaign tracking | Improved lead nurturing, higher engagement rates, increased conversion rates | Automated email sequence triggered by website activity |
| Customer Service | Ticketing system, knowledge base, live chat | Faster response times, improved customer satisfaction, reduced resolution times | Instant live chat support for website visitors |
| Reporting and Analytics | Sales dashboards, custom reports, performance tracking | Data-driven decision making, optimized resource allocation, improved business strategies | Sales performance reports identifying top-performing sales representatives |
Sales Process Workflow Example (Salesforce)
Let’s consider a typical sales process using Salesforce as an example. A potential customer (lead) enters the system through a web form or inbound call. The lead is automatically assigned to a sales representative based on predefined criteria. The sales representative then engages with the lead, documenting all interactions within Salesforce. As the sales process progresses, the lead moves through various stages (e.g., qualified lead, proposal sent, negotiation, closed-won). Salesforce provides tools for tracking opportunities, managing tasks, and forecasting sales. At each stage, relevant information is updated in the system, providing a complete history of the interaction. Once the sale is closed, the information is used for future analysis and forecasting. This entire process is streamlined and tracked within Salesforce, providing valuable insights into sales performance and customer behavior.
Implementation and Integration
Successfully implementing an enterprise CRM system requires careful planning and execution. A phased approach, coupled with robust change management strategies, is crucial to minimize disruption to ongoing business operations and foster widespread user adoption. Integration with existing systems is equally vital for maximizing the CRM’s value and ensuring data consistency across the organization.
Implementing a new enterprise CRM system involves a complex interplay of technical configuration, data migration, user training, and ongoing support. A poorly executed implementation can lead to significant cost overruns, user resistance, and ultimately, failure to achieve the desired business outcomes. Conversely, a well-planned and executed implementation can significantly improve efficiency, enhance customer relationships, and drive revenue growth.
Best Practices for Minimizing Disruption and Maximizing User Adoption
Successful CRM implementation hinges on minimizing disruption and maximizing user adoption. This requires a multi-faceted approach that considers various stakeholders’ needs and expectations. A well-defined project plan, coupled with comprehensive change management strategies, is essential for a smooth transition.
- Phased Rollout: Implement the CRM in stages, starting with a pilot program in a specific department or business unit. This allows for iterative improvements based on feedback and minimizes the risk of widespread issues.
- Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training to all users, covering all aspects of the system. This should include hands-on sessions, online tutorials, and ongoing support.
- Change Management Strategy: Develop a comprehensive change management plan that addresses potential resistance to change. This should include communication strategies, incentives, and ongoing support.
- Data Migration Strategy: Carefully plan the migration of existing data into the new CRM system. This should include data cleansing, validation, and transformation to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involve key stakeholders throughout the implementation process, soliciting feedback and addressing concerns proactively. This ensures buy-in and fosters a collaborative environment.
Integration Options with Existing Business Systems
Integrating a CRM system with existing business systems is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness and avoiding data silos. Various integration methods exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of integration method will depend on factors such as the complexity of the systems, the volume of data, and the budget.
- API Integration: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allow for direct, real-time data exchange between systems. This is generally the most efficient and flexible method, but it requires technical expertise.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): ETL tools extract data from source systems, transform it into a usable format, and load it into the CRM system. This is a suitable approach for large data volumes but may not provide real-time data synchronization.
- Pre-built Connectors: Many CRM systems offer pre-built connectors for popular business applications. These connectors simplify the integration process, but may not be available for all systems.
- Cloud-based Integration Platforms: Cloud-based integration platforms provide a centralized platform for managing integrations between multiple systems. This can simplify the management of complex integrations.
Challenges During CRM Implementation and Mitigation Strategies
Implementing a CRM system can present various challenges. Proactive planning and mitigation strategies are crucial to address these challenges effectively.
- Data Migration Issues: Data migration can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and execution. Data cleansing and validation are crucial to ensure data accuracy.
- User Adoption Challenges: Users may resist adopting a new system, especially if it requires significant changes to their workflows. Comprehensive training and change management strategies are crucial to address this.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the CRM with existing systems can be technically challenging, requiring specialized expertise. Choosing the right integration method is critical.
- Cost Overruns: CRM implementations can be expensive, and cost overruns are common. Careful budgeting and project management are essential to avoid this.
- Lack of Clear Objectives: Without clearly defined objectives, it’s difficult to measure the success of the implementation. Setting clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial.
Step-by-Step Guide for Integrating CRM with Marketing Automation Platform
Integrating a CRM with a marketing automation platform streamlines marketing processes and improves customer data management. This integration allows for automated marketing campaigns based on customer behavior and preferences.
- Define Integration Goals: Clearly define the objectives for integrating the CRM and marketing automation platform. This will guide the selection of integration methods and data fields.
- Select Integration Method: Choose an appropriate integration method based on the systems’ capabilities and the complexity of the integration. API integration is often preferred for its flexibility and real-time capabilities.
- Map Data Fields: Identify the data fields to be shared between the two systems. Ensure consistency in data formats and definitions.
- Configure Integration Settings: Configure the integration settings in both the CRM and marketing automation platform. This typically involves setting up API keys, authentication credentials, and data mapping rules.
- Test the Integration: Thoroughly test the integration to ensure that data is flowing correctly between the two systems. This includes testing data synchronization, automated workflows, and reporting capabilities.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the integration to identify and address any issues. Regularly review and optimize the integration process to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Implementing an enterprise CRM system represents a significant investment, requiring careful consideration of both the upfront costs and the long-term return on that investment. Understanding the various pricing models and calculating potential ROI is crucial for making an informed decision. This section details the factors influencing the total cost of ownership and provides a framework for assessing the financial viability of a CRM implementation.
The financial implications of adopting an enterprise CRM solution extend beyond the initial purchase price. A comprehensive analysis must account for all associated expenses and potential gains to accurately determine the true value proposition.
CRM Pricing Models
Enterprise CRM systems are typically offered using several pricing models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the right model depends heavily on the size of the organization, its specific needs, and its budget.
Understanding these different models is essential for effective budget planning and cost management.
- Subscription-based (SaaS): This model involves recurring monthly or annual payments for access to the CRM software. It often includes features like automatic updates, hosting, and technical support. This is generally the most flexible and cost-effective option for smaller businesses or those with fluctuating needs.
- Perpetual License: With this model, a one-time payment grants a permanent license to use the software. However, ongoing maintenance, support, and upgrades often incur additional costs. This model can be more suitable for larger enterprises with stable requirements and a long-term commitment.
- Hybrid Models: Some vendors offer hybrid models combining elements of both subscription-based and perpetual license models, offering flexibility in terms of licensing and payment schedules. This can be particularly attractive to organizations with diverse needs across different departments or locations.
Calculating ROI for Enterprise CRM
Calculating the ROI of a CRM implementation involves comparing the total costs against the total benefits. While some benefits are easily quantifiable (e.g., reduced customer service costs), others are more challenging (e.g., improved customer satisfaction).
A robust ROI calculation requires careful consideration of both tangible and intangible benefits.
ROI = (Total Benefits – Total Costs) / Total Costs
For example, consider a reduction in customer service calls by 20%, translating to a cost saving of $50,000 annually. This would be a significant component of the total benefits. Other benefits might include increased sales conversion rates, improved lead generation, and better inventory management, all contributing to the overall ROI.
Factors Influencing Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The TCO of a CRM system encompasses a wide range of expenses beyond the initial software license or subscription fees. A comprehensive understanding of these factors is vital for accurate budgeting and cost control.
Failing to account for all TCO components can lead to significant budget overruns and negatively impact the overall ROI.
- Software licensing and subscription fees: This is the most obvious cost, varying depending on the chosen pricing model and the number of users.
- Implementation and customization costs: Professional services for setup, data migration, customization, and training can significantly increase the initial investment.
- Hardware and infrastructure costs: Depending on the deployment model (cloud-based or on-premise), costs for servers, storage, and network infrastructure may apply.
- Ongoing maintenance and support costs: Regular maintenance, updates, and technical support are essential for ensuring optimal system performance and security.
- User training and adoption costs: Investing in comprehensive training programs for users is crucial for successful CRM adoption and maximizing ROI.
Hypothetical ROI Scenario: A Marketing Agency
Let’s consider a mid-sized marketing agency with 50 employees. Currently, they rely on spreadsheets and email for client management, leading to inefficiencies and lost opportunities. Implementing a CRM system could streamline their operations and improve client engagement.
This scenario illustrates the potential for significant ROI through improved efficiency and increased revenue.
| Cost Category | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| CRM Software (Subscription) | $10,000/year |
| Implementation & Customization | $20,000 (one-time) |
| Training | $5,000 (one-time) |
| Total Cost (Year 1) | $35,000 |
| Total Cost (Year 2 onwards) | $10,000 |
| Benefit Category | Estimated Benefit (Annual) |
|---|---|
| Improved client communication & retention (increased revenue) | $25,000 |
| Reduced administrative overhead | $15,000 |
| Improved lead conversion rates | $10,000 |
| Total Annual Benefit (Year 2 onwards) | $50,000 |
In this scenario, the agency achieves a positive ROI starting in Year 2, with annual returns exceeding costs. The initial investment is recouped quickly, demonstrating the potential financial advantages of a well-planned CRM implementation.
Future Trends in Enterprise CRM
The enterprise CRM landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation, driven by advancements in technology and evolving customer expectations. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is fundamentally reshaping CRM capabilities, leading to more personalized, predictive, and efficient customer interactions. This section explores the key future trends shaping the next generation of enterprise CRM solutions.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Enterprise CRM
AI and ML are revolutionizing CRM by automating tasks, improving data analysis, and personalizing customer experiences. AI-powered chatbots provide instant customer support, handling routine inquiries and freeing up human agents for more complex issues. Predictive analytics, driven by ML algorithms, analyze customer data to anticipate future behavior, enabling proactive engagement and personalized offers. For instance, a retail company might use predictive analytics to identify customers likely to churn and offer them targeted incentives to retain their business. This proactive approach, fueled by AI and ML, significantly improves customer retention rates and overall business profitability. Furthermore, AI-powered sentiment analysis can gauge customer satisfaction from various touchpoints, allowing businesses to address negative feedback promptly and improve their services.
Future Trends in CRM Functionality and User Experience
Future CRM systems will be characterized by enhanced functionality and a more intuitive user experience. Expect to see a greater emphasis on seamless integration across all customer touchpoints, creating a unified view of the customer journey. This includes omnichannel capabilities, enabling consistent engagement across various channels like email, social media, and mobile apps. The user interface will become more user-friendly and personalized, adapting to individual user preferences and workflows. The rise of low-code/no-code platforms will empower businesses to customize their CRM systems without extensive coding expertise, making CRM solutions more accessible and adaptable to specific business needs. For example, a marketing team could easily build and deploy customized marketing campaigns directly within the CRM platform, without requiring assistance from IT.
CRM’s Enhanced Role in Customer Relationship Management
In the coming years, CRM will play an even more pivotal role in enhancing customer relationship management. The focus will shift from simply managing customer data to fostering genuine customer relationships. CRM systems will leverage data-driven insights to provide personalized recommendations, anticipate customer needs, and proactively address potential issues. This proactive approach will build stronger customer loyalty and increase customer lifetime value. For example, a financial institution could use CRM data to identify customers who might benefit from a specific financial product and proactively offer it to them, leading to increased sales and improved customer satisfaction. The ability to understand and respond to individual customer preferences and behaviors will become paramount, moving beyond generalized marketing strategies to highly targeted and personalized engagements.
Innovative CRM Applications Shaping Customer Engagement
Several innovative CRM applications are reshaping customer engagement. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are being integrated into CRM systems to create immersive customer experiences, such as virtual product demonstrations or interactive training sessions. The Internet of Things (IoT) is generating vast amounts of data that can be integrated into CRM systems to provide a more comprehensive understanding of customer behavior and preferences. For instance, a smart home device company might use data from connected devices to personalize offers and services based on individual household usage patterns. The use of blockchain technology in CRM could improve data security and transparency, building trust with customers and enhancing data integrity. These innovative applications demonstrate the evolving nature of CRM and its potential to transform customer engagement.
Last Point
Selecting the right enterprise CRM solution is a significant investment, impacting operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall business success. By carefully considering the factors discussed—from functionality and scalability to cost and ROI—enterprises can choose a system that aligns perfectly with their objectives. Embracing the future trends in CRM technology will further optimize processes and strengthen customer relationships, leading to sustainable growth and a competitive edge.